
Hearing loss is a common condition that affects people of all ages. It can be caused by a variety of factors including genetics, age-related wear and tear, noise exposure and certain medical conditions. While it may seem like a minor inconvenience, hearing loss can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
What are the different types of hearing loss?
There are two main types of hearing loss:
- Conductive: This occurs when sound waves are unable to reach the inner ear due to a blockage in the outer or middle ear. Common causes include earwax buildup, ear infections and perforations in the eardrum.
- Sensorineural: This type of hearing loss results from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. It can be caused by exposure to loud noise, ageing, certain medications and genetic factors.
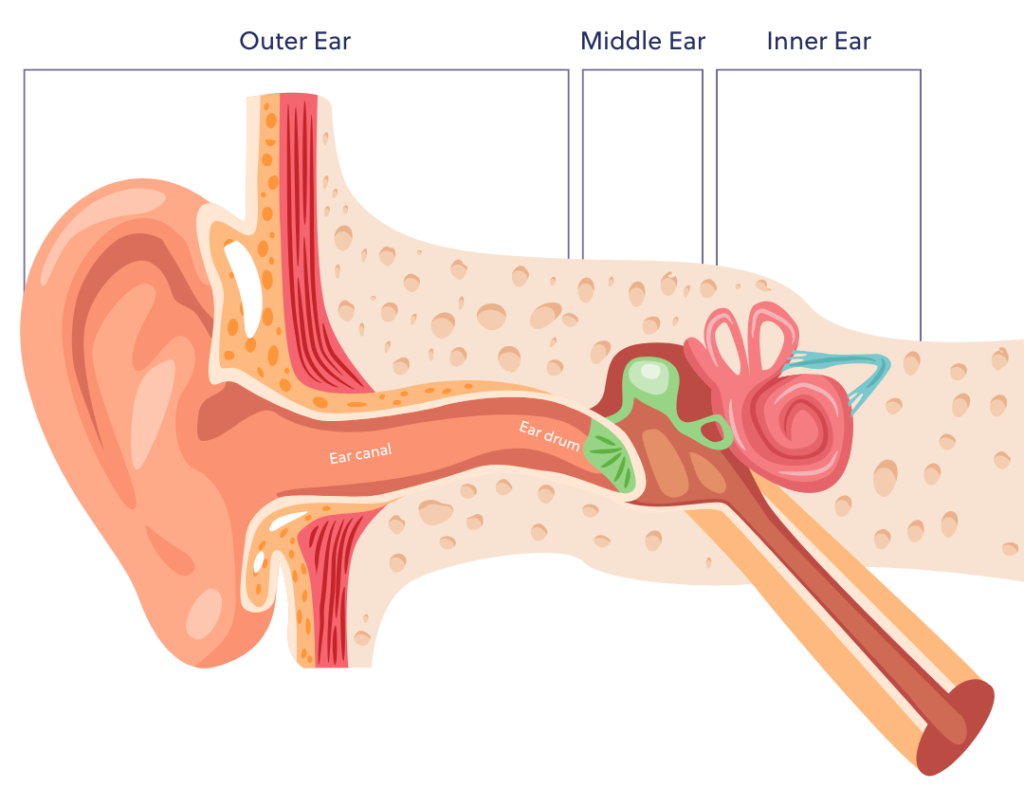
Can you prevent hearing loss?
Hearing loss can have a profound impact on a person’s life, affecting their:
- Social Interactions: Difficulty in understanding conversations, leading to social isolation and loneliness.
- Cognitive Function: Impaired memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
- Emotional Well-being: Increased stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Occupational Performance: Challenges in the workplace, especially in noisy environments or jobs that require clear communication.
While not all types of hearing loss can be prevented, but there are steps you can take to protect your quality of hearing:
- Limit Noise Exposure: Wear earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones when exposed to loud noise.
- Regular Hearing Checkups: Schedule regular hearing tests, especially if you work in a noisy environment or have a family history of hearing loss.
- Manage Underlying Medical Conditions: Treat conditions like ear infections promptly.
What are the treatment options to help improve hearing?
There are several treatment options available to assist you with improving your hearing capabilities. The best treatment option for you will depend on the type, cause and severity of your hearing loss. There are a range of treatment options from medical interventions to assistive technologies, including:
- Hearing aids: a type of assistive technology worn in or behind the ear to amplify sound and are suitable for people with mild to moderate hearing loss.
- Cochlear implants: these are surgically implanted electronic devices that provide a sense of sound to people with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss. Unlike hearing aids, cochlear implants do not amplify sound. Instead, they bypass damaged portions of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
- Assistive listening devices (ALDs): ALDs are devices that can be used in conjunction with hearing aids or cochlear implants to improve hearing in specific situations, such as in noisy environments or during one-on-one conversations.
- Surgical interventions: In some cases, surgical procedures may be needed to treat hearing loss caused by physical issues such as ear infections, ear drum perforations or problems with the ossicles (the bones in the middle ear).
When to seek medical advice
If you suspect you have an issue with your hearing capability, it’s important to seek professional help as early diagnosis and treatment can help minimise the long term impact hearing loss can have on your quality of life.
Find out more information about our Audiology service, or contact our team to book an appointment with an expert Audiologist.
Article produced by:
Sevenoaks Medical Centre